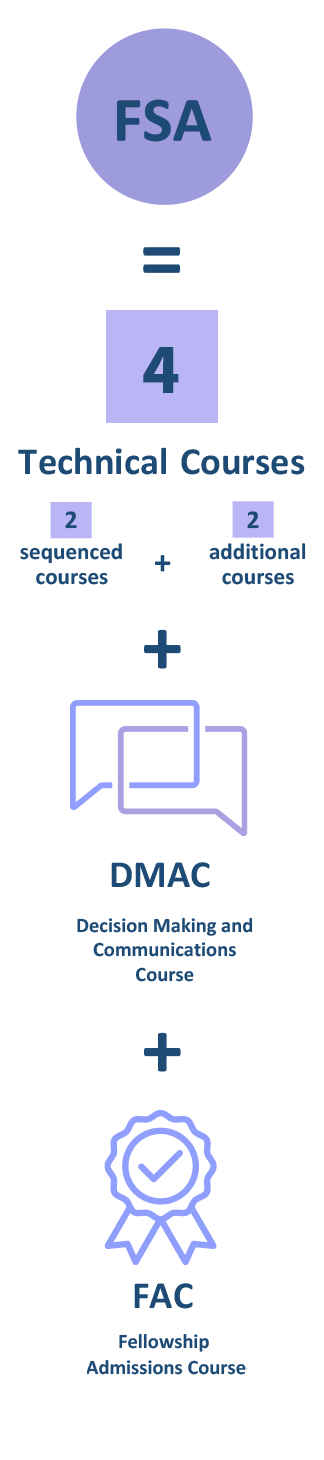
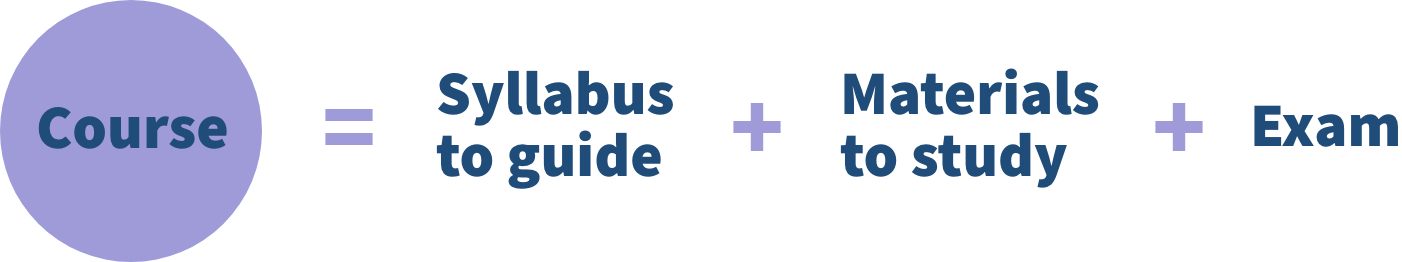
| Corporate Finance and ERM |
CFE 101 Enterprise Risk Management ▼
- Enterprise Risk Management Foundations: Understand the fundamentals of ERM and be able to apply them to organizations.
- Risk Analysis and Evaluation: Understand the types of risks faced by an entity and be able to identify and analyze these risks.
- Embedding ERM into Decision Making: How an organization can articulate its approach to risk and how to assess risk and return trade-offs. The candidate will understand the approaches for managing risk. The candidate will understand different concepts of risk capital, risk measures in capital assessment and techniques to allocate risk capital once aggregated.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
CFE 201 Corporate Finance ▼
- Corporate Finance: Understand how an organization optimizes its corporate finance decisions based on its business objectives.
- Financial Statement Analysis: Gauge an organization’s performance through an evaluation of its financial reports.
- Managerial Accounting and Operational Excellence: Understand how managerial accounting and operational processes impact an organization’s performance evaluation and decision making.
- Evolving Quantitative Methods and Technologies: Understand the appropriate application of evolving quantitative methods and technologies that help to manage the business.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
| Group and Health Insurance |
GH 101 Benefits and Pricing ▼
- Plan & Product Provisions: Understand how to describe plan provisions typically offered under short-duration contracts (medical, dental, vision, prescription drug, group life).
- Manual Rates: Calculate and recommend a manual rate for each of the contracts described in Learning Objective 1.
- Underwriting & Funding: Apply principles of pricing, risk assessment, and funding to an underwriting situation.
- Employee Benefits: Evaluate and recommend an employee benefit strategy.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
GH 201-C Valuation and Regulation, Canada ▼
- Reserving: Apply valuation principles for group and health insurance contracts.
- Financial Statements: Prepare and interpret insurance company financial statements in accordance with IFRS.
- Regulation & Taxation: Evaluate the impact of regulation and taxation on insurance companies and plan sponsors in Canada.
- Government Programs: Describe and evaluate government programs providing health and disability benefits in Canada.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
GH 201-U Valuation and Regulation, U.S. ▼
- Reserving: Apply valuation principles for short duration group and health insurance contracts.
- Financial Statements: How to prepare and interpret insurance company financial statements in accordance with Statutory Accounting Standards and GAAP.
- Regulation: Evaluate the impact of regulation on insurance companies and plan sponsors in the U.S.
- Government Programs: Describe government programs providing health benefits in the U.S.
- Flow of Funds: Describe the flow of funds in the health care system and the role of providers in the system.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
GH 301 Health Analytics and Management ▼
- Provider Contracting and Reimbursement: Evaluate the effectiveness of provider reimbursement methods from both a cost and quality viewpoint.
- Disease Management: Evaluate health care intervention programs.
- Health Care Risk Adjustment: Apply risk adjustment in actuarial work.
- Social Determinants of Health: Explain the determinants of health (SDOH) and their impact on health care costs and policy.
- Medical Data: Describe medical coding, sources of data, and data quality.
- Predictive Analytics: Apply the framework of predictive analytics to health care data and business applications.
- View course page to access they syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
| General Insurance |
GI 101 Ratemaking and Reserving ▼
- Understand key considerations and key concepts underlying general insurance actuarial work.
- Demonstrate the ability to prepare claims and exposure data for general insurance actuarial work.
- Know how to calculate and evaluate projected ultimate values.
- Understand financial reporting of claim liabilities with respect to unpaid unallocated loss adjustment expenses.
- Understand trending procedures as applied to ultimate claims, exposures and premiums.
- Apply the fundamental ratemaking techniques of general insurance.
- Define an approach for actuarial analyses supporting financial reporting and ratemaking analyses under various real-life scenarios.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
GI 201 Operational, Financial, Regulatory and Legal ▼
- Assumes knowledge from GI 101
- Understand the structure and functions of a general insurance company.
- Describe the regulatory environment for general insurance.
- Understand tort law and insurance law with respect to its effect on general insurance.
- Understand elements of financial economics relevant to general insurance.
- Understand the elements of financial reporting for general insurance companies.
- Understand the analysis of a general insurer’s financial health.
- Understand standards of practice and professionalism required of the actuary.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
GI 301 Further Topics in General Insurance ▼
- Assumes knowledge from GI 101
- Use stochastic loss development models to estimate reserve variability.
- Understand the considerations in the development of losses for excess limits and layers.
- Estimate premium liabilities.
- Understand the considerations in selecting a risk margin for unpaid claims.
- Apply methods to monitor actual versus expected experience.
- Understand and apply ratemaking techniques for the following situations: classification ratemaking, deductible options, increased limit options, claims-made policies and individual risk rating.
- Demonstrate knowledge of reinsurance topics including the issues encountered when performing a reserve analysis on reinsurance, how to apply the fundamental techniques of reinsurance pricing and risk transfer testing of reinsurance contracts.
- Understand catastrophe modeling output and the allocation of catastrophe risk loads among accounts.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
GI 302 General Insurance in the U.S. ▼
- Assumes knowledge of GI 101 and GI 201
- Understand the personal lines insurance products offered in the United States.
- Understand common commercial lines insurance products and coverages offered in the United States.
- Understand the development and structure of insurance regulations in the United States.
- Understand the different reporting standards for U.S. general insurance companies and use statutory financial statement information to measure insurer financial health.
- Use applicable standards of practice to carry out the responsibilities of a U.S. signing general insurance actuary as defined by regulators and the American Academy of Actuaries.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
| Individual Life and Annuities |
ILA 101 Pricing and Introduction to Valuation and Risk Management ▼
- Individual Life and Annuity Product Design and Pricing: Understand the designs of the common Life and Annuity products and their associated features and inherent risks, and the methods to design and price these products.
- Assumption Development and Experience Studies: Understand different types of actuarial assumptions and how experience studies are designed and used for evaluating past experience and for setting assumptions.
- Product Management: Understand common issues and practices related to Product Management.
- Introduction to Life and Annuity Valuation Concepts: Understand common valuation and capital techniques used in U.S., Canadian, and international regulatory frameworks.
- Introduction to Assets and Risk Management: Understand various techniques for addressing the mitigation of risk within a life insurance and annuity context.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
ILA 201-I Valuation and Advanced Product and Risk Management, International ▼
- International Financial Reporting Requirements: Understand and apply valuation principles to individual life insurance and annuity products issued by international life insurance companies.
- Capital Management: Understand international capital requirements, the approaches and tools of financial capital management for international life insurance companies.
- Management and Evaluation of Life Insurance Risks: Understand various approaches to manage and evaluate life insurance risks.
- Advanced Product Management: Understand value creation and inforce management techniques for life and annuity products.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
ILA 201-U Valuation and Advanced Product and Risk Management, U.S. ▼
- U.S. Financial Reporting Requirements: Understand and apply U.S. valuation principles and methods applicable to individual life insurance and annuity products issued by U.S. life insurance companies.
- Capital Management: Understand how to explain and apply the methods, approaches and tools of financial capital management for life insurance companies under a U.S. regulatory framework.
- Management and Evaluation of Life Insurance Risks: Understand types of life insurance risks, the impacts of diversification, crediting rating agency frameworks, and the assessment of risk management.
- Advanced Product Management: Understand the fundamentals of value creation and inforce management techniques for life and annuity products.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
| Investment |
INV 101 Portfolio Management ▼
- Asset Classes: Understand the nature and the variety of asset classes that can be used in constructing a portfolio.
- Portfolio Construction, Management, and Assessment: Understand portfolio construction, management, and assessment.
- Credit Risk Management: Understand the best practices of credit risk management.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
INV 201 Quantitative Finance ▼
- Key Types of Derivatives: Understand key types of derivatives.
- Valuation of Derivatives: Understand the principles and techniques for the valuation of derivatives.
- Applications and Risks of Derivatives: Understand various applications and risks of derivatives.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
| Retirement Benefits |
RET 101 Retirement Plan Design ▼
- Benefit Plan Structure, Features and Investments: Analyze different types of designs for retirement plans and retirement plan investments.
- Participant Risks: Analyze the risks faced by retirees and the participants of retirement plans.
- Sponsor Risks: Analyze the risks faced by sponsors of retirement plans.
- Benefit Plan Design Recommendation: Evaluate sponsors’ goals for the retirement plan, evaluate alternative plan types and features, and recommend a plan design appropriate to address those goals.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
RET 201 Retirement Plan Valuation ▼
- Methods: Apply/synthesize the methods and models used to value pension benefits for various purposes.
- Actuarial Assumptions: Analyze/synthesize the factors that go into selection of actuarial assumptions used in pension valuations.
- Accounting Standards: Perform valuations and prepare disclosure information for retirement income plans under applicable accounting standards.
- Investment Risk Management: Recognize and appropriately reflect the role of retirement plan investments in managing plan sponsor risk and make recommendations.
- Valuations for the Purpose of Funding: Understand the general principles applicable to the funding of retirement income plans and recommend a funding policy.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
RET 301 Actuarial Topics for Canadian Retirement Plans ▼
- Assumptions: Analyze/synthesize the factors that go into selection of actuarial assumptions for funding purposes of retirement plans under Canadian pension legislation, regulatory policies, and tax legislation.
- Methods: Prepare valuation results, including required contributions, for various purposes under Canadian pension legislation, regulatory policies, and tax legislation.
- Regulations – Evaluation and Application: Evaluate and apply Canadian pension legislation, regulatory policies, and tax legislation for registered retirement plans.
- Regulations – Plan Funding: Apply the Canadian pension legislation, regulatory policies, and tax legislation in the context of pension plan funding.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
| Cross Practice (relevant to multiple practice areas) |
CP 311 Strategic Management ▼
- Introduction to Strategic Management: Understand and apply strategic management concepts and frameworks to develop an organization’s business strategies and solutions.
- Strategic Budgeting and Value Measures: Understand how sustainable growth and value can be created through strategic budgeting. The candidate will also understand measures of an organization’s value and their uses in decision making.
- Decision Modeling and Optimization: Apply decision-making models to general managerial decisions within specified constraints.
- Organizational Behavior: Understand the role that organizational behavior plays in organizational decision making and efficacy.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
CP 312 Model Development and Governance ▼
- Cash Flow Models for Long-Term Insurance Business: Understand, develop, apply, and evaluate cash flow models for various types of long-term insurance business. The candidate will demonstrate an understanding of the underlying modeling methodologies: their strengths, limitations, and applications.
- Non-Cash Flow and Supplementary Models for Financial Business: Understand, apply, and evaluate non-cash flow and supplementary models for various types of long-term insurance business. The candidate will demonstrate an understanding of the underlying methodologies: their strengths, limitations, and applications.
- Model Governance: Understand and be able to apply appropriate model governance to assess and address issues common to the development and management of models.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
CP 321 Disability, Long-Term Care, and Long-Duration Health Contracts ▼
- Plan & Product Provisions: Describe benefits typically offered under long-duration contracts (disability income, long-term care, critical illness, Medicare Supplement).
- Manual Rating: Calculate rates for each of the contracts described in Learning Objective 1.
- Reserving: Apply valuation principles for long-duration contracts.
- Financial Statements: Prepare and interpret insurance company financial statements for long duration contracts.
- Retiree Group Benefits: Design and perform valuations of Retiree Group Benefits.
- Asset Adequacy: Apply asset matching and asset adequacy standards as they apply to long duration contracts.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
CP 341 Advanced Life Reinsurance ▼
- Types of Reinsurance Arrangements and Methods: Understand different types of traditional and advanced reinsurance transactions for life insurance.
- Transferring Risk: Understand the fundamentals of risk transfer between two counterparties.
- Key Accounting and Regulatory Considerations: Understand regulatory frameworks for reinsurance transactions across US, Canadian, and global jurisdictions.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|
CP 351 Asset Liability Management ▼
- Objectives of Asset Liability Management: Understand the objectives of Asset Liability Management (ALM).
- Measuring Risk from Assets and Liabilities: Understand how to measure risks from assets and liabilities.
- Tools and Strategies to Manage ALM Risks: Understand tools and strategies to manage ALM risks.
- View course page to access the syllabus and see the enhancements.
|